Hackers targeting Google Bard ads for malware
Hackers targeting Google Bard ads for malware
The Rise of AI Cyberattacks: Google Bard Chatbot Targeted by Hackers
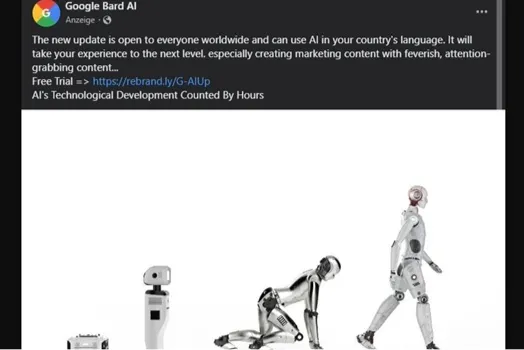 Image Source: ESET Research / ESET Research
Image Source: ESET Research / ESET Research
As artificial intelligence becomes more prevalent in our lives, there is a growing concern about the potential for hackers to exploit this technology. The latest target of these cybercriminals is the Google Bard chatbot, which is being used as a decoy to trick unsuspecting users into downloading malware.
The ads promoting Google Bard are designed to appear safe and trustworthy, mimicking the style of Google’s official advertisements. However, upon clicking on these ads, users are directed to a webpage infected with malware, instead of an official Google page.
Security researchers at ESET were the first to notice the discrepancies in these ads. They found several grammar and spelling errors, as well as a writing style that did not match Google’s standard. These clues helped them identify the malicious intent behind these ads. According to TechRadar, accessing these malware-ridden webpages while being logged into browser accounts could potentially expose users’ private data to hacking attempts.
The ads also include a download button, which, when clicked, downloads a file disguised as a personal Google Drive space. In reality, this file is a confirmed malware known as GoogleAIUpdate.rar. ESET researcher Thomas Uhlemann warned that variations of this campaign were still visible as of Monday, indicating the scale and persistence of the cyberattack.
This is not the first time an AI chatbot has been targeted by hackers. OpenAI’s ChatGPT chatbot experienced a similar cyberattack earlier this year. Security researcher Dominic Alvieri discovered a website called chat-gpt-pc.online, which hosted an info-stealing malware disguised as ChatGPT. This website even featured ChatGPT branding and was promoted on a Facebook page to deceive users into accessing the infected site.
Moreover, Alvieri also found fake ChatGPT apps on Google Play and various third-party Android app stores. These apps had the ability to deliver malware to devices if downloaded. It appears that bad actors have targeted ChatGPT extensively, especially since its introduction of the ChatGPT Plus tier, which costs $20 per month. In some instances, hackers have even used the chatbot to create and distribute their own malware. These specially crafted versions of OpenAI’s GPT-3 API generate malicious content, including phishing emails and malware scripts.
The Google Bard chatbot represents a growing trend in cybercrime, where hackers exploit the trust people place in AI technology. As AI becomes more intertwined with our daily lives, it is crucial for both developers and users to remain vigilant and adopt robust security measures. It is through collective effort that we can ensure the potential of AI brings positive advancements, without falling prey to its darker side.






